Predictive Modeling Helps Focus Retention Marketing Resources
Is it possible to know one’s customers better than they themselves do? When it comes to next-purchase or defection behavior, marketers can use predictive modeling techniques to identify target populations most likely to respond positively to a variety of efforts.
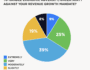
Consider the contrast of a campaign focused with great precision through predictive modeling with a randomly targeted mailing. Predictive modeling might determine that the top 10 percent of customers by revenue represent the top 30 percent of customers likely to leave for a competitor. This information yields a readymade list of targets for retention efforts.
Without this information, a company would treat all customers equally and risk wasting retention campaigns on happy (or less profitable) customers or—even worse—losing key customers by failing to address their concerns. Getting it right benefits the company through:
- Increased response rate as a result of contacting the right customers, which reduces campaign costs by targeting those most likely to respond.
- Maximized revenue by understanding what customers will buy lets companies design campaigns accordingly.
- Increased revenues through understanding a customer’s propensity to buy specific products or the sequential order of purchases.
- Higher customer retention, growth, and acquisition as a result of understanding the target population and conveying relevant messages.
Applying Predictive Models to Marketing Strategy
Predictive modeling helps marketers execute outreach strategy and achieve pre-set business objectives. Before selecting a model a marketer should consider the following questions, which will offer insight into the best treatment strategy:
- Why will my customer attrite?
- When will my customer attrite?
- Who is saveable?
- Who will buy? What will they buy?
- Which product will they buy next?
- When will they buy?
There are a number of modeling techniques available to help give direction to marketers’ thinking. Rather than there being a single correct answer, each offers strengths based on the goals of a campaign. For instance:
- Decision tree modeling: Using this strategy, a population is split into subgroups which are more homogeneous than the original sample. Subsetting continues until the model cannot be improved, or until subgroups have too-small a population to effectively target.
- Clustering: Under this approach, individuals are grouped based on geographic proximity with the expectation that their demographic similarities will be reflected in behavioral similarities.
- Logistic regression modeling: This generalized linear model calculates the probability of a particular customer being a member of a target group based on the values of predictor fields selected by a marketer. These predictor fields can consist of either observed data, such as transactions, or implicit data, such as demographics.
- Survival modeling: These are used for determining time-to-event for one-time happenstances. This model is used to study retention trends by demographic area, channel, credit class, rate plan, and type of churn, or to estimate remaining lifetimes for present customers. A marketer could answer the question, “When will customers attrite?” using a survival model that identifies customers who will likely leave for a competitor within three months, six months, or a year and take preventive steps.
Larry Mosiman is global product manager for SAS Customer Intelligence.